
Īs an alternative, if we restrict the model to linear Gaussian optics, we could use spherocylindrical vergences instead of spherical vergences, or equivalently we could use 4 × 4 matrix algebra instead of 2 × 2 matrices to address spherocylindrical surfaces with random axes.

Once crossed cylinders are involved, this simplification into a 2-step calculation is no longer applicable-for instance, in cases with an arbitrary spherocylindrical target refraction, measurement data from the corneal back surface where the astigmatic axis is not fully aligned to the corneal front surface astigmatism, a surgically induced astigmatism (SIA), or any correction strategy for corneal back surface astigmatism which is not reflected by keratometry. This works quite well provided the optical model does not involve crossed cylinders. With most of the classical calculation concepts, toric intraocular lenses (tIOL) can be easily calculated in 2 separate steps for the two cardinal meridians of the cornea: in the first, we calculate the lens power for the flat corneal meridian, and in the second, the respective lens power is calculated for the steep corneal meridian. But as with theoretical-optical formulae, the axial position of the IOL has to be estimated empirically prior to cataract surgery.
#Itrace toric lens alignment full#
Full aperture ray tracing concepts such as Okulix use tomographic data from the corneal front and back surface together with design data for the IOL front and back surface provided by the IOL manufacturer to trace a bundle of rays from the object to the retinal image plane in order to calculate an appropriate lens power. Theoretical-optical formulae are mostly based on paraxial vergence calculation using linear Gaussian optics, where the effective lens position of the lens implant (mostly simplified with a thin lens model) is estimated by empirical means. Empirical concepts include the simple regression formula such as the SRK or SRK2 formula, and also modern strategies of machine learning such as the PEARL (Prediction Enhanced Artificial intelligence and output Linearization ) or the Hill-RBF (Radial Base Function) calculator. Some of these calculation concepts are purely empirical, others are so-called theoretical-optical formulae, and others are based on full aperture ray tracing.
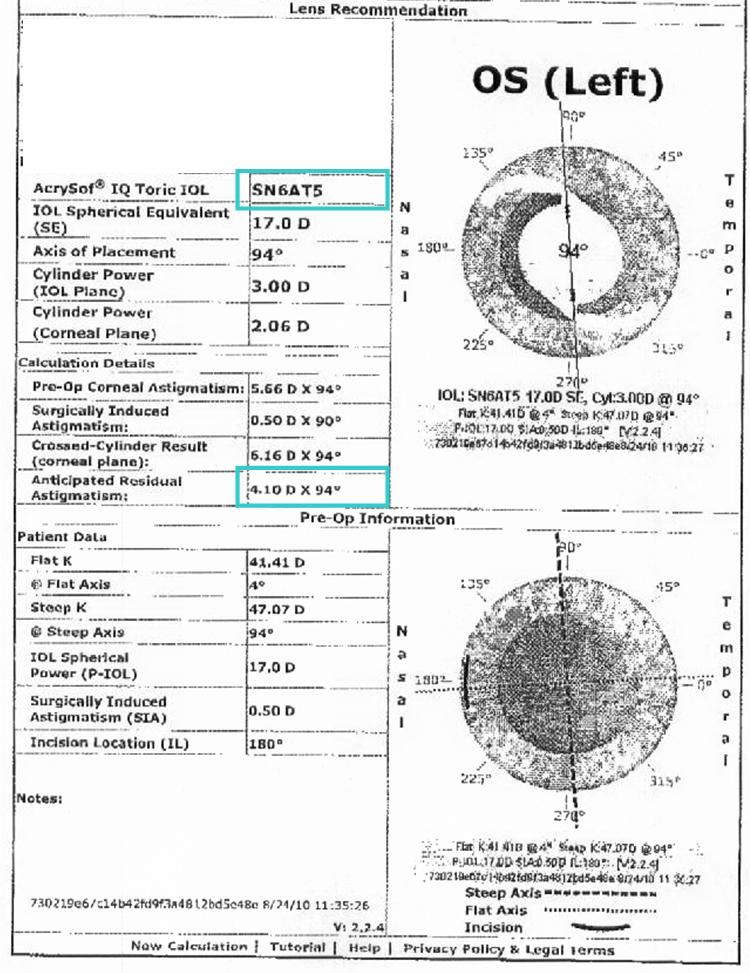
Since then, a wide range of formulae have been proposed by different scientists. The first intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation formulae were published in 1967 by Fyodorov and independently in 1970 by Gernet, Ostholt, and Werner. The application in clinical studies is needed to prove the potential of this new concept. The Castrop formula for toric lenses is a generalization of the Castrop formula based on spherocylindrical vergences. In the 3rd example, we predicted the spherocylindrical power of spectacle refraction after implantation of any toric lens with an inverse calculation. In the 2nd example, we calculated the tIOL power with keratometric data from corneal front surface measurements, and considered a surgically induced astigmatism and a correction for the corneal back surface astigmatism. In the 1st example, we derived the tIOL power for a spherocylindrical target refraction and corneal tomography data of corneal front and back surface. Three clinical examples are presented to show the applicability of this calculation concept.
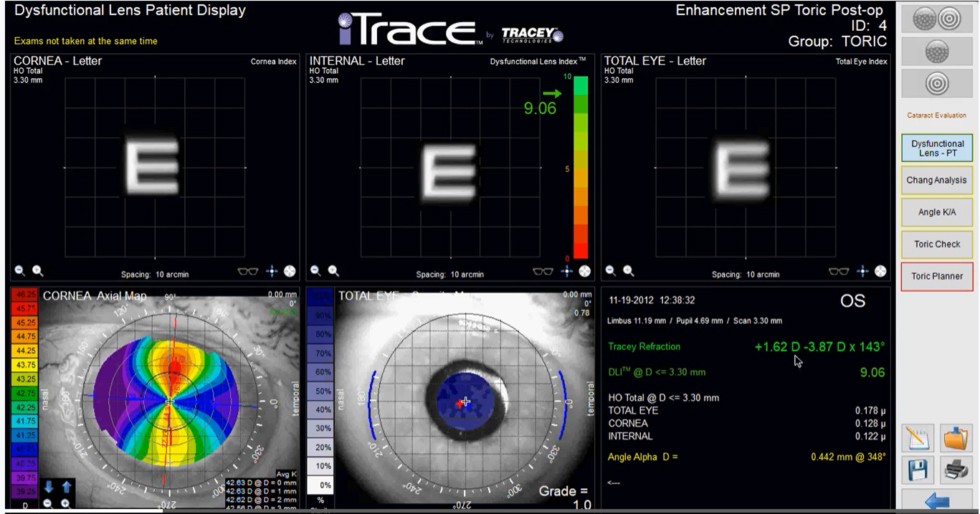
Spectacle correction can be predicted with an inverse calculation. With front surface data only, the back surface is defined from the front surface and a fixed ratio of radii and corneal thickness as preset.

With tomographic data for the corneal front and back surface, these data are considered to define the thick lens model for the cornea exactly. All four surfaces (spectacle correction, corneal front and back surface, and toric lens implant) are expressed as spherocylindrical vergences. The Castrop vergence formula is based on a pseudophakic model eye with four refractive surfaces and three formula constants. To explain the concept behind the Castrop toric lens (tIOL) power calculation formula and demonstrate its application in clinical examples.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
